UNICEF: Water Quality Continues to be a Challenge
china.org.cn by Victoria Cole, June 24, 2015 Adjust font size:
United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), along with the National Working Committee on Children and Women (NWCCW) and the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), has published the 2014 "Children in Asia: An Atlas of Social Indicators", providing perspectives of the various situations of children in China.
With the help of many visual aids, this fourteen-section publication reports relevant socio-economic information, reflecting China's achievements and disparities for children and serves as a "comprehensive and detailed resource for relevant government departments, child rights practitioners and the general public."
Water, Sanitation and Hygeine (Section 7)
For nearly three decades, beginning with its participation in the First International Decade on Safe Drinking Water and Environmental Sanitation (1981–1990), China has worked with the international community to improve rural water supply and sanitation by building water supply plants, introducing appropriate water and sanitation technologies and building the institutional capacity of the Government.
In 2007:
- 17% of schools in the country had no water supply.
- Less than 38% of schools equipped with a water supply met the national drinking water quality standard.
- 32% of schools were equipped with sanitary latrines.
The Eleventh Five-Year National Development Plan (2006–2010) led to an increase in central Government expenditure on rural water supply, rising to more than 20 billion per year in 2009-onward. However, the poorer areas of the western and central provinces need particular attention, as they are often unable to allocate local matching funds to fully implement programmes that only receive partial funding from the central Government.
In 2010:
- China achieved the sanitation-related MDG target.
- 31% of township hospitals had indoor toilets.
- Only 55% of township hospitals with indoor toilets had handwashing facilities.
Extreme climatic conditions, caused by global climate change, occur more and more frequently and pose risks to the security of water supply. Environmental degradation often makes safe water supply and sanitation solutions more costly.
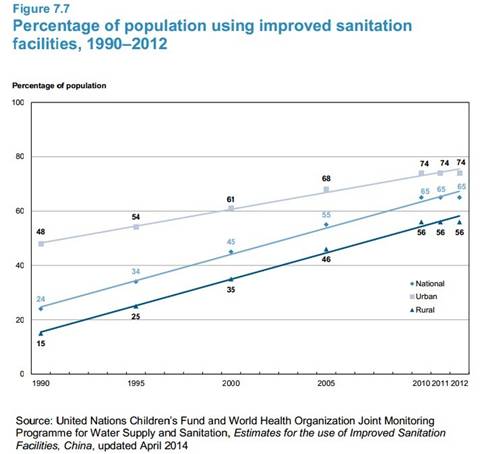
"Improvements in rural sanitation are supported by general fund transfers from the central Government to local budgets":
Rural sanitation was included in the Health Sector Reform Programme started from 2009, with an annual allocation of around RMB 1.6 billion to support improvements in rural household sanitation, such as the eradication of schistosomiasis (an endemic disease which can be spread by improper management of livestock and human waste) and the agriculture sector's biogas programme.
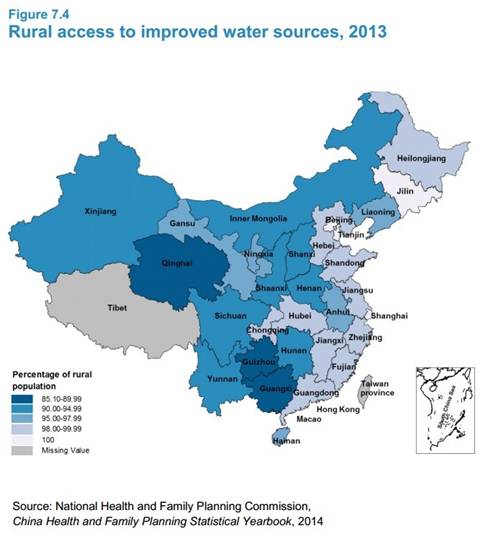
"Water quality continues to be a challenge":
Drinking water sources are becoming scarcer, and the treatment of water has become increasingly costly. Both surface water and groundwater are contaminated in many areas by industrial and human activities, and arsenic and fluoride poisoning and schistosomiasis pose particular problems.